
-

生物通官微
陪你抓住生命科技
跳动的脉搏
Arraystar rG4芯片:解锁RNA动态结构奥秘
【字体: 大 中 小 】 时间:2025年12月16日 来源:康成生物
编辑推荐:
Arraystar rG4芯片技术不仅能够有效捕获和检测活细胞中的rG4,同时也消除了DMS诱导的修饰所产生的偏差,从而显著提高了rG4 定量图谱分析结果的准确性和可靠性。
一、简介
RNA G-四联体 (RNA G-quadruplexes,rG4)是由富含鸟嘌呤 (G) 的RNA序列通过Hoogsteen氢键形成的一种非经典二级结构。该结构由堆叠的G-四分体平面构成,并由K⁺等单价阳离子稳定(图1)。rG4的动态结构转变可调控RNA转录[1]、染色质修饰因子募集[2]、miRNA前体加工[3]、mRNA翻译[4, 5]以及 mRNA 稳定性[6]。此外,rG4 还能与m7G [3]、o8G[7]和m6A[8, 9]等 RNA 修饰共同调控基因表达。rG4形成发生失调,则会影响应激反应 [7]、癌症基因表达调控 [10, 11],并与帕金森病、路易体痴呆及多系统萎缩中发生的α-突触核蛋白聚集有关[12]。
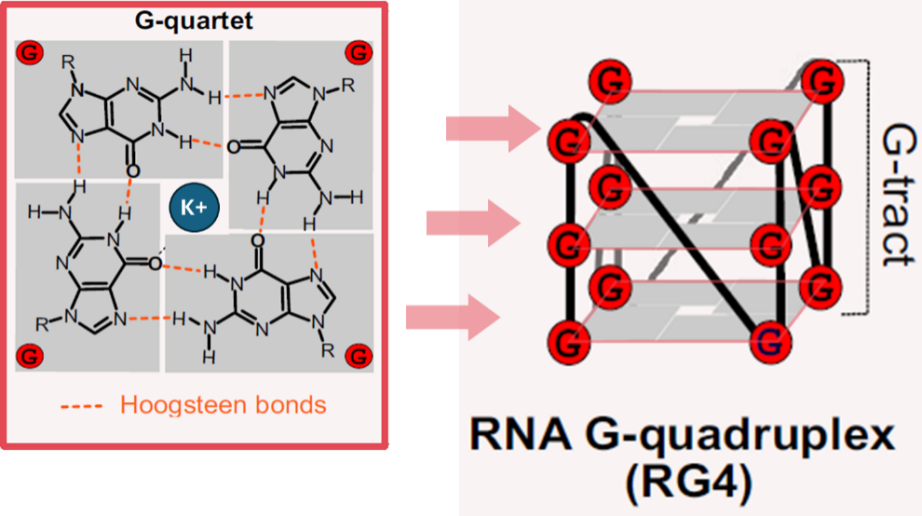
图1. 在富含鸟嘌呤的RNA序列中,四个鸟嘌呤通过Hoogsteen键结合形成G-四分体平面,G-四分体平面堆叠形成RNA G-四联体(RG4)[13]。
Arraystar rG4芯片技术可精准定量转录组中的rG4 结构。其中的关键步骤包括:体内硫酸二甲酯 (Dimethyl sulfate, DMS) 处理、体外RNA重折叠,以及使用抗G4抗体(BG4)进行亲和性捕获。随后,将捕获到的含有 rG4结构的 RNA进行去甲基化处理,以去除 DMS 处理所产生的副产物m1A/m3C,消除其造成的检测干扰。最后,利用高灵敏度的Arraystar rG4 芯片探针对rG4-RNA进行定量分析。Arraystar rG4芯片技术不仅能够有效捕获和检测活细胞中的rG4,同时也消除了DMS诱导的修饰所产生的偏差,从而显著提高了rG4 定量图谱分析结果的准确性和可靠性。

二、技术优势
体内DMS处理与体外重折叠复现了真实的rG4结构
使用高亲和性的BG4抗体特异性富集含有rG4结构的RNA
Demthylation处理去除了DMS 处理的副产物m1A/m3C所造成的检测干扰
Arraystar 芯片可以灵敏的检测rG4 RNA, 包括RNA测序无法准确检测的低丰度RNA
三、实验流程
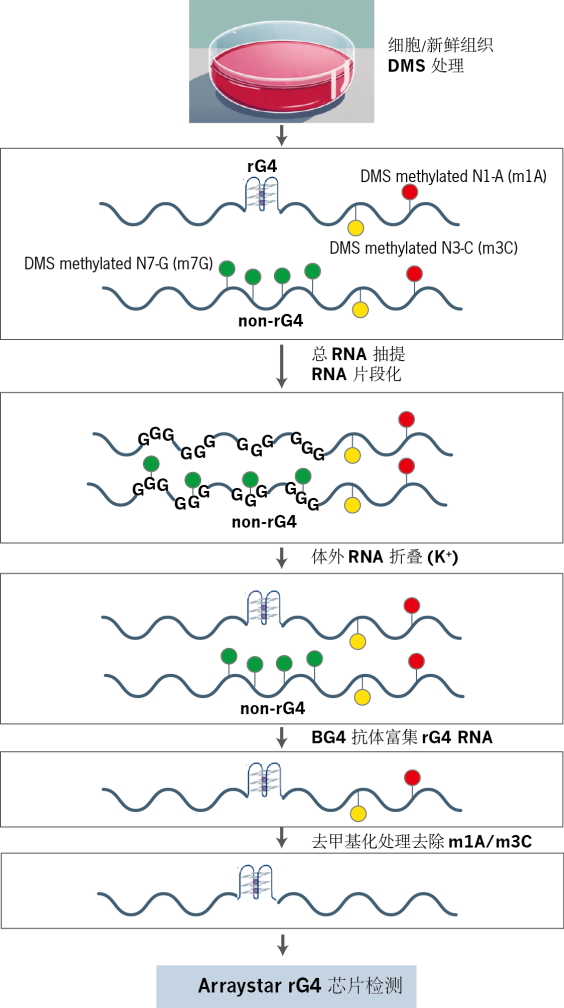
图2. rG4芯片实验流程图。
1. 体内 DMS 处理
培养细胞经硫酸二甲酯(DMS)处理,对 RNA 中的腺嘌呤(A)、胞嘧啶(C)及非 rG4折叠区域的鸟嘌呤(G)进行甲基化修饰。rG4 结构内的 G 碱基因空间位阻不受影响,从而保留其未甲基化状态。
2. RNA 抽提与体外重折叠
分离总 RNA 并进行片段化处理,随后在含K⁺的缓冲体系中经历变性-复性过程。此步骤仅允许细胞内原有的 rG4 区域特异性重折叠,而其他区域由于携带m7G修饰,无法形成稳定结构。
3. rG4 免疫沉淀
利用抗 G-四联体抗体(BG4)对含 rG4 结构的 RNA 进行免疫沉淀(IP),实现目标分子的特异性富集。
4. 去甲基化与反转录
富集的 RNA 经去甲基化酶处理,清除 DMS 诱导的副产物(如 m¹A/m³C),消除检测偏差。随后通过反转录合成双链 cDNA,并引入T7 启动子序列。
5. 荧光标记 cRNA 合成
以 cDNA 为模板,T7 RNA 聚合酶催化体外转录反应,掺入Cy3-CTP 荧光染料,生成带Cy3 标记的反义 cRNA。
6. 芯片杂交与数据分析
标记的 cRNA 与Arraystar rG4 芯片杂交,通过荧光信号定量分析转录组中rG4 结构的分布与丰度。
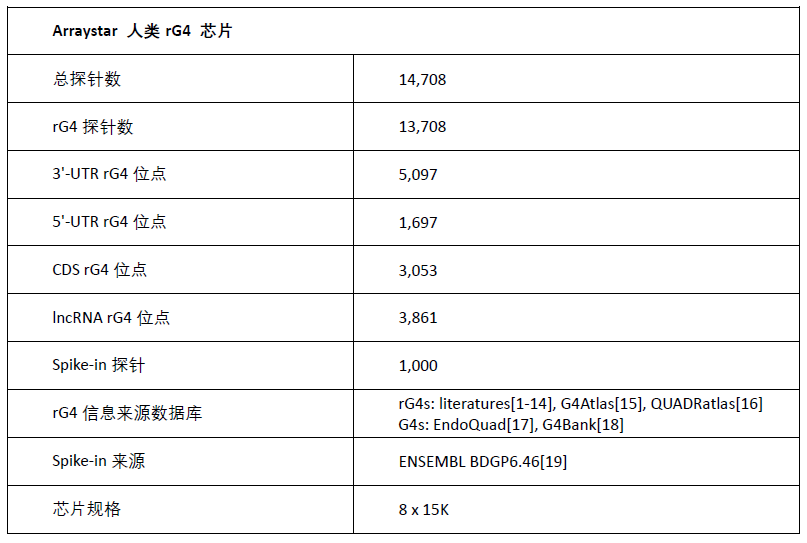
四、芯片参数
Arraystar 人类 rG4 芯片参数
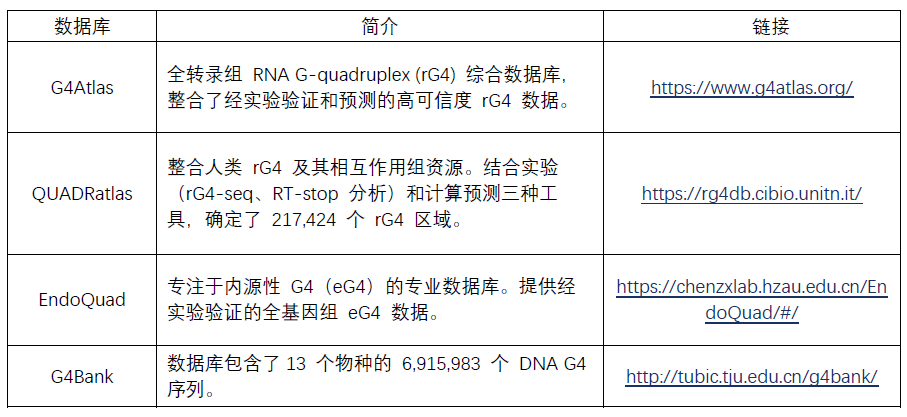
RNA G-quadruplex (rG4) 数据库
参考文献
1. Yari H et al: LncRNA REG1CP promotes tumorigenesis through an enhancer complex to recruit FANCJ helicase for REG3A transcription. Nat Commun 2019, 10(1):5334.[PMID: 31767869]
2. Lee YW, Weissbein U, Blum R, Lee JT: G-quadruplex folding in Xist RNA antagonizes PRC2 activity for stepwise regulation of X chromosome inactivation. Mol Cell 2024, 84(10):1870-1885 e1879.[PMID: 38759625]
3. Pandolfini L et al: METTL1 Promotes let-7 MicroRNA Processing via m7G Methylation. Mol Cell 2019, 74(6):1278-1290 e1279.[PMID: 31031083]
4. Arora A, Suess B: An RNA G-quadruplex in the 3' UTR of the proto-oncogene PIM1 represses translation. RNA Biol 2011, 8(5):802-805.[PMID: 21734463]
5. Song J, Perreault JP, Topisirovic I, Richard S: RNA G-quadruplexes and their potential regulatory roles in translation. Translation (Austin) 2016, 4(2):e1244031.[PMID: 28090421]
6. Rouleau S et al: 3' UTR G-quadruplexes regulate miRNA binding. RNA 2017, 23(8):1172-1179.[PMID: 28473452]
7. Ma Y et al: RNA G-Quadruplex within the 5'-UTR of FEN1 Regulates mRNA Stability under Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants (Basel) 2023, 12(2).[PMID: 36829835]
8. Yoshida A et al: Recognition of G-quadruplex RNA by a crucial RNA methyltransferase component, METTL14. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50(1):449-457.[PMID: 34908152]
9. Jara-Espejo M, Fleming AM, Burrows CJ: Potential G-Quadruplex Forming Sequences and N(6)-Methyladenosine Colocalize at Human Pre-mRNA Intron Splice Sites. ACS Chem Biol 2020, 15(6):1292-1300.[PMID: 32396327]
10. Anastasakis DG et al: Nuclear PKM2 binds pre-mRNA at folded G-quadruplexes and reveals their gene regulatory role. Mol Cell 2024, 84(19):3775-3789 e3776.[PMID: 39153475]
11. Kharel P, Ivanov P: PKM2-G-quadruplex interactions conspire to regulate the cancer transcriptome. Mol Cell 2024, 84(19):3574-3575.[PMID: 39366344]
12. Matsuo K et al: RNA G-quadruplexes form scaffolds that promote neuropathological alpha-synuclein aggregation. Cell 2024, 187(24):6835-6848 e6820.[PMID: 39426376]
13. Dumas L et al: G-Quadruplexes in RNA Biology: Recent Advances and Future Directions. Trends Biochem Sci 2021, 46(4):270-283.[PMID: 33303320]
14. Kwok CK et al. rG4-seq reveals widespread formation of G-quadruplex structures in the human transcriptome. Nat. Methods 13, 841–844 (2016).
15. Yang SY et al. Transcriptome-wide identification of transient RNA G-quadruplexes in human cells. Nat. Chem. Biol. 14, 180–183 (2018).
16. Yeung PY et al. Systematic evaluation and optimization of the experimental steps in RNA G-quadruplex structure sequencing. Sci. Rep. 9, 8091 (2019).
17. Weng X et al. Keth-seq for transcriptome-wide RNA structure mapping. Nat. Chem. Biol. 16, 489–492 (2020).
18. Hansel-Hertsch R et al. G-quadruplex structures mark human regulatory chromatin. Nat. Genet. 48, 1267–1272 (2016).
19. Herviou P et al. hnRNP H/F drive RNA G-quadruplex-mediated translation linked to genomic instability and therapy resistance in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 11, 2661 (2020).
20. Simko EAJ et al. G-quadruplexes offer a conserved structural motif for NONO recruitment to NEAT1 architectural lncRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, 7421–7438 (2020).
21. Bolduc F et al. The small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide A (SNRPA) binds to the G-quadruplex of the BAG-1 5'UTR. Biochimie 176, 122–127 (2020).
22. Guo JU et al. RNA G-quadruplexes are globally unfolded in eukaryotic cells and depleted in bacteria. Science. Sep 23;353(6306):aaf5371 (2016).
23. von Hacht A et al. Identification and characterization of RNA guanine-quadruplex binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. Jun;42(10):6630-44 (2014).
24. Haeusler et al. C9orf72 nucleotide repeat structures initiate molecular cascades of disease. Nature 507, 195–200 (2014).
25. McRae EKS et al. Human DDX21 binds and unwinds RNA guanine quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. Jun 20;45(11):6656-6668 (2017).
26. Serikawa T et al. Comprehensive identification of proteins binding to RNA G-quadruplex motifs in the 5' UTR of tumor-associated mRNAs. Biochimie. Jan;144:169-184 (2018).
27. Herdy B et al. Analysis of NRAS RNA G-quadruplex binding proteins reveals DDX3X as a novel interactor of cellular G-quadruplex containing transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. Nov 30;46(21):11592-11604 (2018).
28. Yu H et al. G4Atlas: a comprehensive transcriptome-wide G-quadruplex database. Nucleic Acids Res. Jan 6;51(D1):D126-D134 (2023).
29. Bourdon S et al. QUADRatlas: the RNA G-quadruplex and RG4-binding proteins database. Nucleic Acids Res. Jan 6;51(D1):D240-D247 (2023).
30. Qian SH et al. EndoQuad: a comprehensive genome-wide experimentally validated endogenous G-quadruplex database. Nucleic Acids Res. Jan 5;52(D1):D72-D80 (2024).
31. Zhong HS et al. G4Bank: A database of experimentally identified DNA G-quadruplex sequences. Interdiscip Sci. Sep;15(3):515-523 (2023).
32. Birney E et al: An overview of Ensembl. Genome Res. May;14(5):925-8 (2004).
官网:www.aksomics.com
电话:800-820-5058 400-886-5058 021-64451989
地址:上海市闵行区陈行公路2168号浦江智慧广场10C幢4楼