
-

生物通官微
陪你抓住生命科技
跳动的脉搏
免疫检查点抑制剂心肌与肌肉毒性的发病率及风险因素:一项法国全国性研究
【字体: 大 中 小 】 时间:2025年09月01日 来源:European Heart Journal 35.6
编辑推荐:
本研究针对免疫检查点抑制剂(ICI)治疗中罕见但致命的心肌炎和肌炎并发症,通过分析法国全国健康数据库172,363例患者数据,首次系统评估了ICI相关心肌毒性(0.7%-0.9%)和肌炎(0.3%-0.6%)的发病率,发现胸腺癌患者风险最高(sHR 12.94),并证实其与死亡率显著相关(HR 3.51)。研究为临床风险分层提供了关键证据,发表于《European Heart Journal》。
免疫检查点抑制剂(Immune checkpoint inhibitors, ICI) revolutionized cancer treatment by unleashing T-cell antitumor activity. However, this breakthrough came at a cost - the immune system could also attack healthy tissues, particularly the heart and skeletal muscles. Among these immune-related adverse events (irAEs), myocarditis and myositis emerged as rare but devastating complications, with mortality rates reaching up to 50% in early reports. The clinical landscape presented a critical knowledge gap: while case reports and small series highlighted the severity of ICI-associated myotoxicities, robust epidemiological data on incidence, risk factors, and prognostic impact remained scarce, particularly in real-world populations beyond clinical trials.
To address this unmet need, Joe-Elie Salem and colleagues conducted a landmark pharmacoepidemiological study leveraging the French National Health Data System (SNDS), encompassing nearly the entire French population. This retrospective cohort analysis included all adult cancer patients initiating ICI therapy between 2012-2022 (n=172,363), employing both narrow and broad definitions for myotoxicity outcomes based on ICD-10 codes. The research team implemented sophisticated statistical approaches including Fine and Gray competing risk models and time-dependent Cox regression to account for mortality as a competing risk.
Key methodologies included:
National database analysis using French SNDS covering 99% population with linkage of hospitalization and pharmacy claims data
Two-tiered outcome definitions (narrow/broad) for myotoxicity, myocarditis and myositis using ICD-10 codes
Multivariable regression adjusting for demographics, comorbidities, cancer types and treatments
Time-to-event analysis with competing risk modeling
Main Results
Incidence and Risk Factors
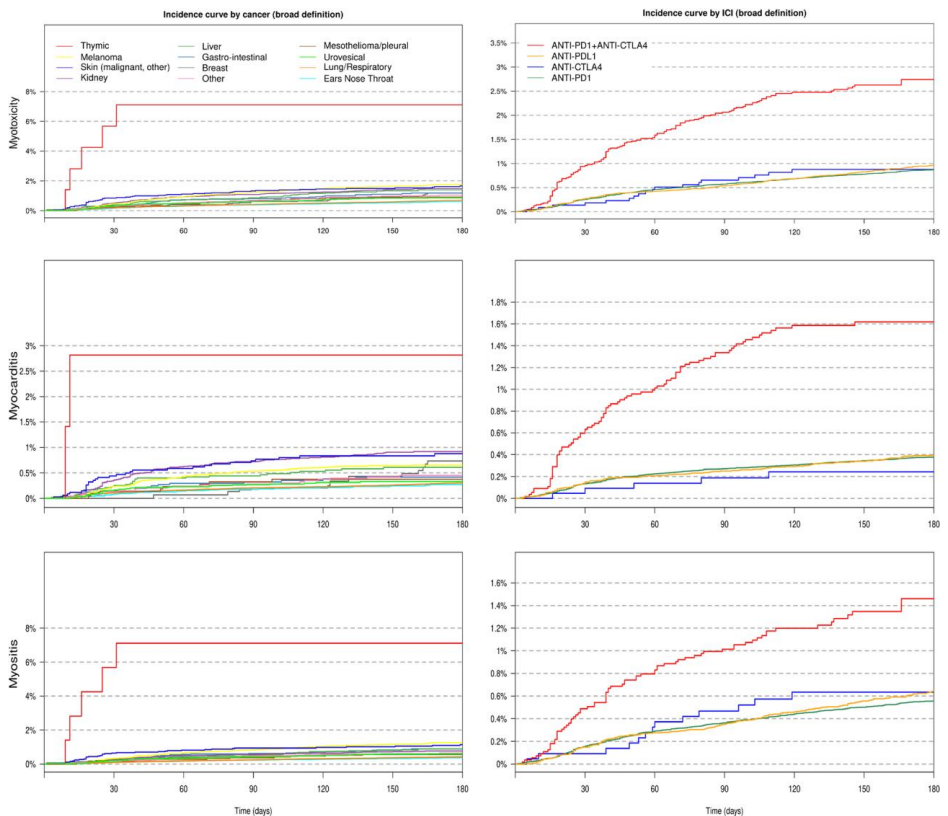
The 6-month cumulative incidence of ICI myotoxicities ranged 0.7%-0.9%, with striking variation by cancer type - from 0.5% in ENT cancers to 7.1% in thymic malignancies. Myocarditis and myositis showed substantial overlap (13%-23% co-occurrence). Multivariable analysis revealed:
Extreme risk with thymic cancer (sHR 12.94) and history of thymic disorders (sHR 5.61)
Significant associations with melanoma (sHR 2.41), other skin cancers (sHR 2.07), and myasthenia gravis history (sHR 2.50)
ICI combination therapy doubled risk (sHR 2.44) versus anti-PD1 monotherapy
Age >85 years showed 79% increased risk versus younger patients
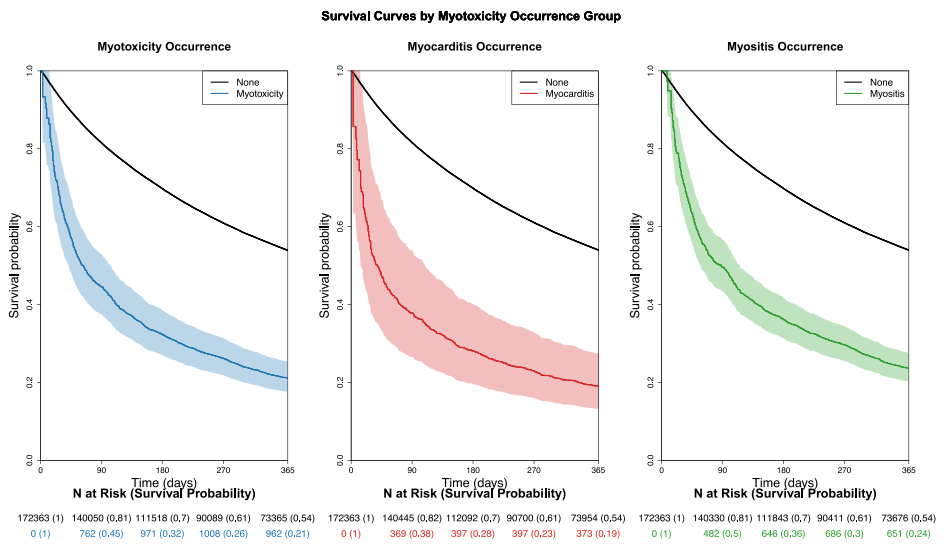
Survival Impact
Myotoxicity emergence dramatically worsened prognosis, becoming the strongest mortality predictor post-ICI initiation:
1-month survival: 54% (no myotoxicity) vs 21% (with myotoxicity)
Time-varying HR peaked at 3.51 within first month, remaining elevated at 3.07 by 90 days
Exceeded metastatic status impact (HR 1.55)
Fatality Predictors
Among myotoxicity cases (n=1,520), 1-month fatality reached 20.3%, significantly associated with:
Severe arrhythmia/conduction disorders (RR 1.64)
Concurrent heart failure (RR 1.49) and respiratory failure (RR 1.50)
Anti-CTLA4 monotherapy showed 2.3-fold higher fatality versus anti-PD1
This seminal work establishes the first comprehensive epidemiological profile of ICI-related myotoxicities in a real-world setting. The findings carry profound clinical implications:
Validates thymic involvement as central to pathophysiology, supported by extreme risks in thymic cancer and history of thymic disorders
Provides quantitative risk estimates to guide monitoring strategies, particularly for high-risk groups (elderly, skin cancer patients, combination therapy recipients)
Confirms the critical prognostic value of early cardiac/respiratory complications
Demonstrates consistent results across analytical methods and outcome definitions, reinforcing robustness
The study's national-scale design overcomes limitations of prior fragmented evidence from clinical trials and single-center cohorts. By illuminating both the epidemiology and clinical consequences of these life-threatening complications, this research fundamentally advances risk mitigation strategies in immuno-oncology practice. The identification of thymic-related risk signatures also opens new avenues for mechanistic investigation into shared autoimmunity pathways between myositis and myocarditis.
These findings immediately inform clinical practice by enabling risk-adapted monitoring protocols and underscore the urgent need for interdisciplinary collaboration between oncologists and cardiologists. As ICI indications continue expanding into earlier disease settings and combination regimens, the study's risk stratification framework will prove invaluable for optimizing the benefit-risk balance of these transformative cancer therapies.
 生物通微信公众号
生物通微信公众号
知名企业招聘